The Importance of Fine Motor Skills for Children's Development
Fine motor skills refer to the ability to control the movements of small muscles, typically in the hands and fingers, to accomplish precise tasks. It is an important skill for children as it enables them to perform daily life tasks such as writing, manipulating small objects, and engaging in hands-on activities.
At Wesco, our collection of fine motor skill games has been specially designed to allow children from early childhood to the age of 6 to work on the precision of their movements and abilities, and to develop dexterity while playing with our educational games. Our products are particularly suited for learning and strengthening the abilities of young children to perform precise gestures that require concentration and patience. Hand-eye coordination will be greatly enhanced, allowing young players to consolidate the movements of different body parts involved in each type of game. For example, magnetic puzzles help to work on shoulder stability, as well as the various hand manipulations required to properly place each piece in the right spot.
Fine Motor Skill Games for Children: A Wesco Collection Specifically Designed
Lacing games typically involve the use of cords, laces, or ribbons to thread through holes or eyelets. Lacing games can be made from different types of materials and have varying levels of difficulty to suit each child's age and skill level. They help develop fine motor skills, improve children's concentration, self-confidence, and autonomy. Here are some examples of
lacing games for children :
Shoe lacing: This involves threading laces through the eyelets of a shoe and tying them to fasten the shoe. It can help children learn to tie their shoelaces and develop their hand-eye coordination.
String drawing: This involves threading a string or cord through holes or eyelets on a card or wooden panel. Children can then use the string to create drawings or shapes by threading it through different holes.
Precision Games to Improve Children's Coordination and Concentration
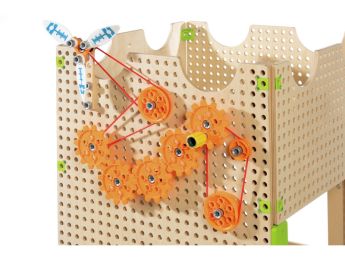
Precision games are games that require coordination and precision skills from children. They can help improve hand-eye coordination, fine motor skills, and concentration. There are many types of precision games such as manipulation games, balance games, and coordination games.
These
precision and balance games allow children to improve their spatial perception. By stacking blocks or shapes of different sizes, they learn to recognize shapes and sizes and understand how these elements fit together to form a stable structure.
Children's Activity Cubes: Educational Toys to Develop Motor and Cognitive Skills
Children's activity cubes are educational toys designed to help children develop their motor and cognitive skills. They are often made of wood or plastic and feature various activities on each side.
The activities on
activity cubes can include mazes, puzzles, gears, stacking shapes, abacuses, mirrors, buttons to press, switches to toggle, doors to open, and fasteners to manipulate.
These toys offer numerous benefits for young children, such as: Improvement of hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills. Development of shape, colour, and texture recognition. Reinforcement of problem-solving and logical thinking. Enhancement of attention and concentration. They are suitable for children aged 6 months to approximately 3 years, depending on the models.
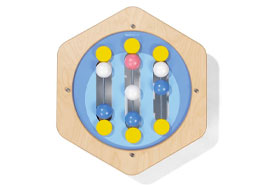
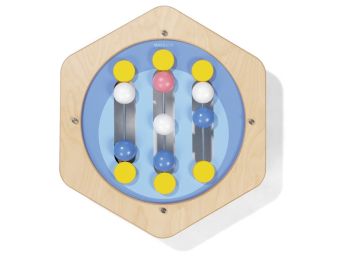
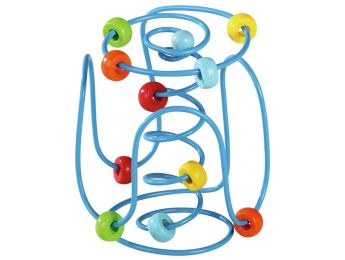
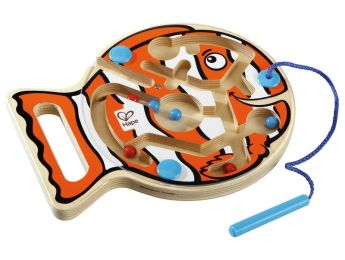
Children's Bead Mazes: A Fun Game to Develop Fine Motor Skills and Concentration
Bead mazes are educational games that involve balls rolling along a series of tracks or tubes, usually made of wood or plastic. These games allow children to develop their hand-eye coordination, fine motor skills, and concentration while having fun.
There are many types of bead maze games for children, ranging from simple models with a single track to more complex ones with multiple tracks and balls.
Children's
bead maze games are often colorful and generally suitable for children of all ages, although more complex models may be better suited for older children. They are often used to encourage children's cognitive development.